Reasonably not possible to meet the demand or to build enough new roads.
Make the system of transportation more efficient, safer and secure through the use of information, control and communications technologies.
Gain the attractiveness of public transport.
Tackle rising overcrowding which increases industry costs and travel times.
Lessen the environmental impacts of transportation.
Advantages of Intelligent Transportation System
— Travel time improvement.
— Capacity management.
— Incident management.
— Reduction in stops and stoppages at intersections.
— Speed improvement and better control.
How Intelligent Transportation System Works?
ITS combining technologies:
The technical core of an intelligent transportation system (ITS) is the control technologies and application of information to transportation system operations. These technologies include automatic control, computer hardware, software and communications.
ITS Enabling Technologies:
There is a range of communications and information technologies that enable ITS development like fibre optics, CD-ROM, electromagnetic compasses, GPS, etc.
Data Acquisition:
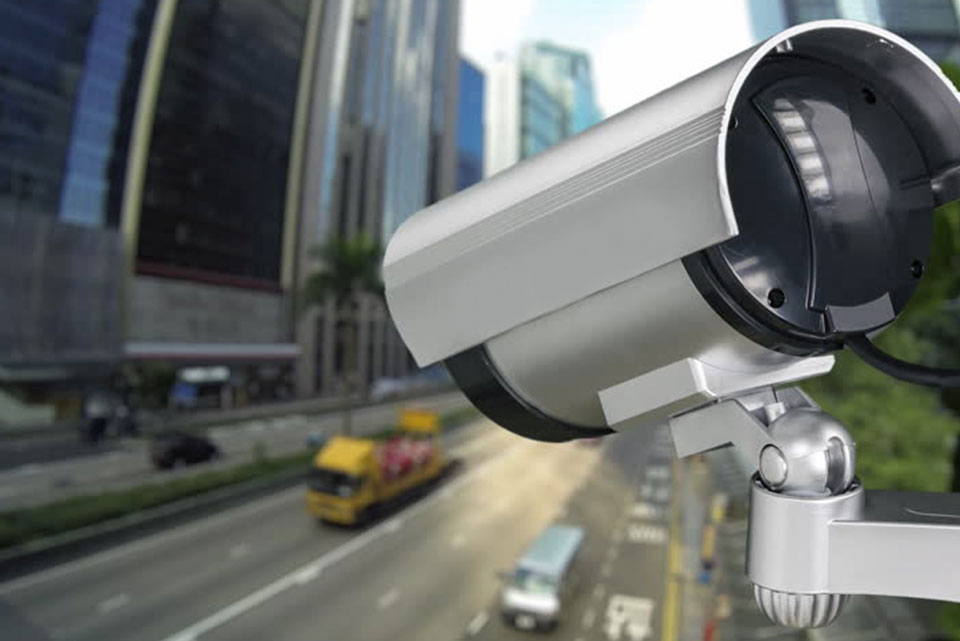
– Using several means, it is possible to monitor traffics such as inductive loop detectors, traffic sensor. Examples: radar and ultrasonic, visual images from closed-circuit television (CCTV) and video image detector (VID).
Data Processing:
– Information accumulated at the data management centre needed to be concocted, verified and strengthened into a format that useful for the operators.
Data Communications:
– Different ways can be practised to convey messages, for example, Fibre optics, electronic toll collection (ETC), wireless or wireline, commercial vehicle operations (CYO), signal preemption, parking management, etc.
Data Distribution:
– Traffic and other similar information can be shared in various ways in order to improve transportation safety, environmental quality and efficiency.
Information Utilisation:
– This comprises ramp metering to control the stream of vehicles blending onto an expressway, and coordination of traffic control within huge urban areas occurs at the traffic management centre.
System Architecture:
Framework for defining, planning, and combining intelligent transportation systems.
Benefits of Architecture:
– Reduces resources and time required to combine the technologies to local needs.
– Help identify jurisdictions and agencies & seeks their cooperation.
Intelligent transportation user services are provided:
– Traveller Information
– Public Transport
– Emergency Management
– Electronic Payment (EP) Safety
– Traffic Management
– Vehicle Systems
– Commercial Vehicles